We called Greg Carr the other day to talk about the spread of the coronavirus in Africa. Carr, who has been featured in Nautilus, is the founder of the Gorongosa Restoration Project, a partnership with the Mozambique government to revive Gorongosa National Park, that environmental treasure trove at the southern end of the Rift Valley. The 1,500 square-mile park, about the size of Rhode Island, was first given animal refuge status in the 1920s by the Portuguese, and for years was a favorite of European tourists. But in 1983 civil war broke out and the park became a no-man’s land. The place was poached to death, closed up and didn’t reopen until 1992.
Renewal began in 2004 and in 2008 the government signed a restoration agreement with Carr’s foundation. The agreement, which lasts through 2043, envisions a “human rights park” that will restore both ecosystems and economic vitality. After 11 years of rebuilding infrastructure, reintroducing animals, including hippos and wildebeests, and working with local communities, Gorongosa is thriving again. The park now serves as a model for future conservation. Today some 200,000 people live around the park in a “sustainable development zone” that includes education, employment opportunities, and health service. About 700 people have full time jobs in the park; another 300, part time. Naturalist E.O. Wilson calls Gorongosa “a window on eternity.”
“If there’s one thing the rest of the world can learn from Africans, it would be their resilience.”
Carr is a 60-year-old entrepreneur and philanthropist who grew up in Idaho and in his mid twenties co-founded Boston Technology, a voice mail company. By the time he turned 40 he had amassed his fortune and couldn’t see the fun in doing it all over again, and so turned to philanthropy. These days he’s in Idaho Falls, on the phone six hours a day, getting the latest reports from his staff in the park, now closed until further notice.
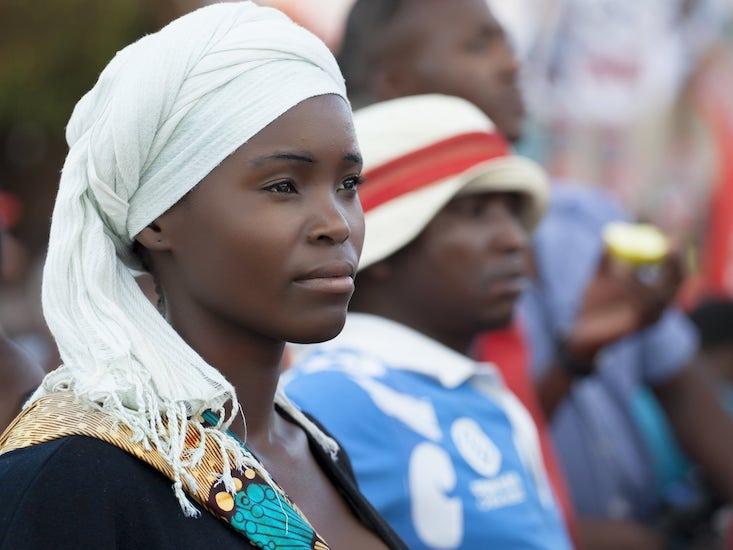
The coronavirus news from Mozambique is mixed, as it is in much of sub-Saharan Africa. With the exception of South Africa, with over 7,500 confirmed cases of COVID-19 and 148 deaths, some countries below the Equator have fewer than 100 cases. As of May 6, there were just 81 cases in Mozambique and no deaths. If these numbers don’t blow up, the quick explanation might hold that the median age in Sub Saharan Africa is under 20, just 17.6 in Mozambique; population density is low (103 people per square mile); and there’s relatively limited direct contact with heavily infected countries in other parts of the world.
Still, many experts fear chaos is inevitable. Underlying conditions in Mozambique include implacable poverty and a 60-year history of colonial and civil wars. On another front, in early April, in northern Mozambique, an Isis group shot or beheaded 52 young people because they refused to be recruited. Add a 48 percent literacy rate for women, 60 percent for men. The country also suffers the world’s eighth-highest incidence of HIV; 1.5 million people have contracted the virus and nearly 40,000 people have died. Finally, a large number of Mozambicans go to South Africa for work and then return. Testing is rare in the entire country.
In March, CDC Africa sent out a national directive requiring social distancing. “People are going to pay more attention to that in the cities than they are in rural Mozambique, at least until the virus really comes,” Carr said the other day. “Now, if you live in rural Mozambique, you don’t have the luxury of saying, ‘I’m isolating at home.’ People have to go out every day, to get food and water, from 40 to 60 liters a day, they have to tend to their farms. The idea of social distancing is a bit impossible for these folks.” He added, “Schools are closed and we are making our own masks for people. We all know there’s no treatment per se or certainly vaccine. If this hits, we’ll only be able to offer people Tylenol and soup.”
Cases in Mozambique could shoot up as mine workers continue to return home from their jobs in South Africa. “In my opinion,” said Carr, “Mozambique does not have the capacity to deal with this type of pandemic, as there are few qualified health personnel and the high level of poverty leads people to resist isolating themselves, as they look for alternatives to take care of their families. Our Gorongosa teams are in the field, spreading prevention messages, distributing masks and water purification.”
Berta Barros, head nurse at Gorongosa, told Carr recently she has three main worries: lack of COVID-19 test kits, lack of healthcare professionals to respond to sick patients, and shortage of medications for treatment. “Mozambique has a population close to 30 million and we only have 34 ventilators,” Barros said. “It’s beyond impossible to work and choose who to save.”
Carr often talks about Mozambique as though he was Mozambican. “We’re very practical people,” he’ll say. “We’re not really theoretical. We’re just going to work our way through this.” He shies away from broad, open-ended questions about Africa, much less cultural comparisons and grand conclusions. “Africa is more than 1 billion people in 54 countries with, what, 2,500 languages? To make a statement like, ‘Africa is this…’ Frankly, I just think a lot of it is complete baloney.”
At the same time, says Carr, “If there’s one thing the rest of the world can learn from Africans, it would be their resilience. We’ve had five years of war in Mozambique and then last year we had a cyclone that killed nearly 1,000 people. I didn’t even mention the two droughts we had in the last seven years and the armyworm that came through and ate everybody’s maize. These people had their homes washed away in a flood last year, lost everything. So they rebuild their homes and then someone says, ‘Hey, there might be a virus coming through.’ It’s just one thing after another.”
What impact might the pandemic have on animals in the park? What effect will it have on just recovered antelope populations, for example, and the inevitable increase in poaching as tourism subsides? How many resources will need to be taken away from the war on other diseases to fight this? Impossible to say. But an anecdote came to Carr’s mind that suggests the vagaries of death in Southern Africa. “I got a call from a dear friend of mine yesterday, a Mozambique good friend, who said her aunt had just died. I said, ‘Wow, do you think it was COVID?’ She goes, ‘No, she’d been suffering for a while with a bad kidney.’ Life is tough in Africa. Do we know for sure this woman didn’t also have COVID and that contributed? Maybe. The truth about Africa is that disaster is hardly news. Malaria is the most prolific killer. And when they turn 50, people die and often no one knows exactly what the cause was. It’s just the way life is.”
Mark MacNamara is an Asheville, North Carolina-based writer. His articles for Nautilus include “We Need to Talk About Peat” and “The Artist of the Unbreakable Code.”