Jordana Cepelewicz
“Traffic Jams” of Cells Help to Sculpt Embryos
By measuring mechanical forces inside an embryo for the first time, researchers have shown how a physical “jamming” mechanism assists development.
Why Nature Prefers Couples, Even for Yeast
Some species have the equivalent of many more than two sexes, but most do not. A new model suggests the reason depends on how often they mate.
Chronological Clues to Life’s Early History Lurk in Gene Transfers
To date the branches on the evolutionary tree of life, researchers are looking at horizontal gene transfers among ancient microorganisms, which once seemed only to muddle the record.
Complex Animals Led to More Oxygen, Says Maverick Theory
that new animal behaviors raised oxygen levels and remade the environment.
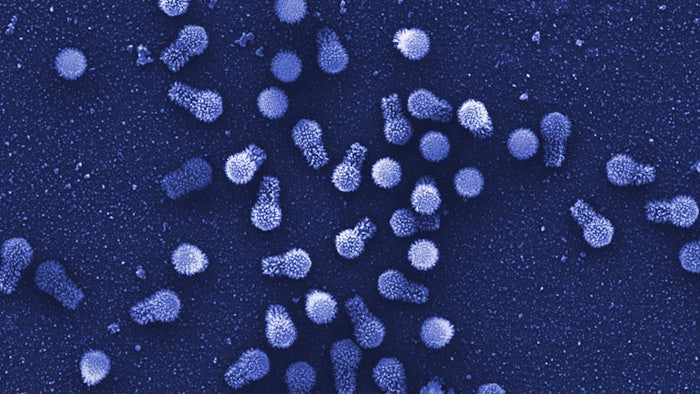
New Giant Viruses Further Blur the Definition of Life
A newfound pair of giant viruses have massive genomes and the most complete resources for building proteins ever seen in the viral world. They have refreshed the debate about the origins of these parasites.
With Strategic Zaps to the Brain, Scientists Boost Memory
Stimulating part of the cortex as needed during learning tasks improves later recall. The finding reveals more about the brain’s memory network and points toward possible therapies.
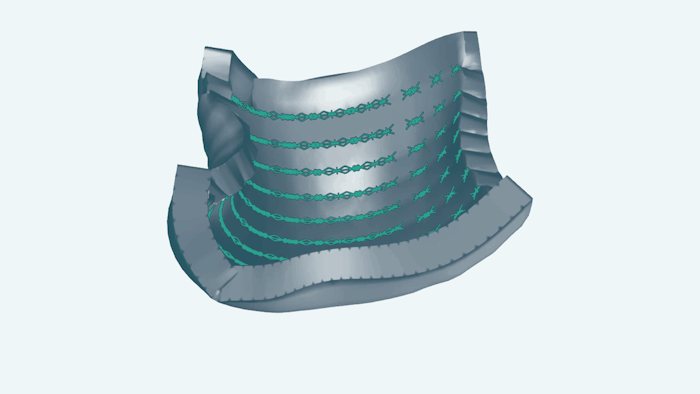
Tissue Engineers Hack Life’s Code for 3-D Folded Shapes
Mechanical tension between tethered cells cues developing tissues to fold. Researchers can now program synthetic tissue to make coils, cubes and rippling plates.
With ‘Downsized’ DNA, Flowering Plants Took Over the World
Compact genomes and tiny cells gave flowering plants an edge over competing flora. This discovery hints at a broader evolutionary principle.
New Bird Species Arises From Hybrids, as Scientists Watch
The rapid, unorthodox emergence of a new finch in the Galápagos hints that speciation isn’t rare. New hybrid species may quietly appear and disappear without anyone noticing.
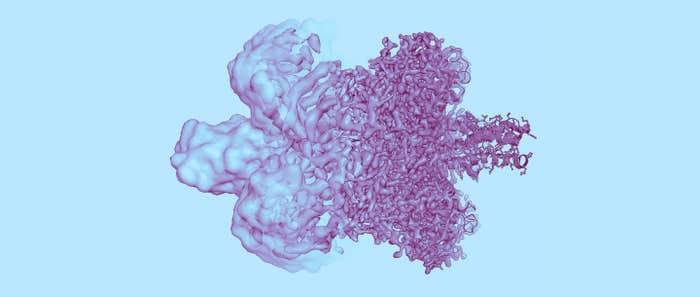
Supercool Protein Imaging Gets the Nobel Prize
This year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry goes to researchers who made it possible to see proteins and other biomolecules at an atomic level of detail.