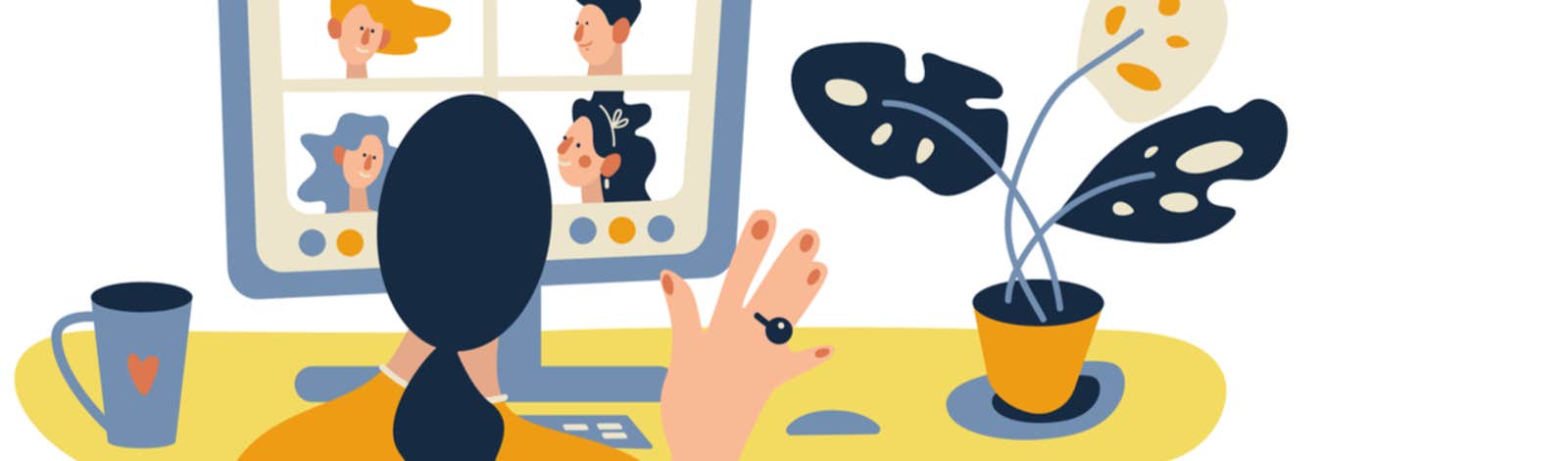
My mother-in-law, Carol, lives alone. It was her 75th birthday the other day. Normally, I send flowers. Normally, she spends some part of the day with the family members who live nearby and not across the country as my husband, Mark, and I do. And normally, she makes plans to celebrate with a friend. But these are not normal times. I was worried about sending a flower delivery person. Social distancing means no visiting with friends or family, no matter how close they are. So, my sister-in-law dropped off a gift and Mark and I sang “Happy Birthday” down the phone line with our kids. But I could hear the loneliness in Carol’s voice.
This was hardly the worst thing anyone experienced in America on that particular April day. We are fortunate that Carol is healthy and safe. But it upset me anyway. People over 60 are more vulnerable to COVID-19 than anyone else. They are also vulnerable to loneliness, especially when they live alone. By forcing us all into social isolation, one public health crisis—the coronavirus—is shining a bright light on another, loneliness. It will be some time before we have a vaccine for the coronavirus. But the antidote to loneliness is accessible to all of us: friendship.
Those who valued friendship as much as family had higher levels of health and happiness.
All too often we fail to appreciate what we have until it’s gone. And this shared global moment has illuminated how significant friends are to day-to-day happiness. Science has been accumulating evidence that friendship isn’t just critical for our happiness but our health and longevity. Its presence or absence matters at every point in life, but the cumulative effects of either show up most starkly in the later stages of life. That is also the moment when demographics and health concerns can conspire to make friendships harder to find or sustain. As the world hits pause, it’s worth reminding ourselves why friendship is more important now than ever.
Friendship has long been understood to be valuable and pleasurable. Ancient Greek philosophers enjoyed debating its virtues, in the company of friends. But friendship has largely been considered a cultural phenomenon, a pleasant by-product of the human capacity for language and living in groups. In the 1970s and 1980s, a handful of epidemiologists and sociologists began to establish a link between social relationships and health. They showed those who were more socially isolated were more likely to die over the course of the studies. In 2015, a meta-analysis of more than 3 million people whose average age was 66 showed that social isolation and loneliness increased the risk of early mortality by up to 30 percent.1 Yet loneliness and social isolation are not the same thing. Social isolation is an objective measure of the number and extent of social contact a person has day to day. Loneliness is a subjective feeling of mismatch between how much social connection you want and how much you have.
Once the link between health and relationships was established in humans, it was noticed in other species as well. Primatologists studying baboons in Africa remarked that when female baboons lost their primary grooming partners to lions or drought, they worked to build bonds with other animals in place of the one they’d lost. When the researchers analyzed the social behavior of the animals and their outcomes over generations, they found in multiple studies that the animals with the strongest social networks live longer and have more and healthier babies than those that are more isolated.2 Natural selection has resulted in survival of the friendliest.
Since baboons don’t drive each other to the hospital, something deeper than social support must be at work. Friendship is getting “under the skin,” as biologists say. Some of the mechanisms by which it works have yet to be explained, but studies have demonstrated that social connection improves cardiovascular functioning, reduces susceptibility to inflammation and viral disease, sharpens cognition, reduces depression, lowers stress, and even slows biological aging.3
We also now have a clearer definition of what friendship is. Evolutionary biologists concluded that friendship in monkeys—as well as people—required at least three things: it had to be long-lasting, positive, and cooperative. When an anthropologist looked for consistent definitions of friendship across cultures, he found something similar. Friendships were described as positive, and they nearly always include a willingness to help, especially in times of crisis. What friendship is about at the end of the day is creating intensely bonded groups that act as protection against life’s stresses.4
Social connection reduces depression, lowers stress, and even slows biological aging.
That buffering effect is particularly powerful as we age. Those first epidemiology studies focused on people in the middle of life. In 1987, epidemiologist Teresa Seeman of the University of California, Los Angeles, wondered if age and type of relationship mattered for health.5 She found that for those under 60, whether or not they were married mattered most. Being unmarried in midlife put people at greater risk of dying earlier than normal. But that did not turn out to be true for the oldest groups. For those over 60, close ties with friends and relatives mattered more than having a spouse. “That was a real lightbulb that went on,” Seeman says.
In a 2016 study, researchers at the University of North Carolina found that in both adolescence and old age, having friends was associated with a lower risk of physiological problems.6 The more friends you had, the lower the risk. By contrast, adults in middle age were less affected by variation in how socially connected they were. But the quality of their social relationships—whether friendships provided support or added strain—mattered more. Valuing friendship also proved increasingly important with age in a 2017 study by William Chopik of Michigan State University. He surveyed more than 270,000 adults from 15 to 99 years of age and found that those who valued friendship as much as family had higher levels of health, happiness, and subjective well-being across the lifespan. The effects were especially strong in those over 65. As you get older, friendships become more important, not less; whether you’re married is relatively less significant.7
There’s a widespread sense, especially among younger people, that people are lonely post-retirement. The truth is more complicated. Social networks do get smaller later in life for a variety of reasons. In retirement, people lose regular interaction with colleagues. Most diseases, and the probability of getting them, worsen with age. It’s more likely you will lose a spouse. Friends start to die as well. Mental and physical capacities may diminish, and social lives may be limited by hearing loss or reduced mobility.
Yet some of this social-narrowing is intentional. If time is of the essence, the motivation to derive emotional meaning from life increases, says Laura Carstensen, director of the Stanford Center for Longevity. She found that people choose to spend time with those they really care about. They emphasize quality of relationships over quantity. While family members fill much of a person’s inner social circle, friends are there, too, and regularly fill in in the absence of family. A related, more optimistic perspective on retirement is that with fewer professional and family obligations, there are more hours for the things we want to do and the people with whom we want to do them.
At all stages of life, how we do friendship—whether we focus on one or two close friends or socialize more widely—has to do with our natural levels of sociability and motivation. Those vary, of course. I recently spoke with a man who had retired to Las Vegas. When he and his wife moved to their new house, his wife began baking cookies and distributing them to neighbors. She started throwing block parties for silly holidays and those neighbors showed up. No one had bothered to organize such a thing before. Even in retirement, this woman is what psychologists call a “social broker”—someone who brings people together. She has most likely always been friendly.
What best predicted health wasn’t cholesterol levels, but satisfaction in relationships.
How you live your life before you reach 60 makes a difference, experts on aging say. Friendship is a lifelong endeavor, but not everyone treats it that way. Think of relationships the way we do smoking, says epidemiologist Lisa Berkman of Harvard University. “If you start smoking when you’re 14, and stop smoking when you’re 65, in many ways, the damage is done,” she says “It’s not undoable. Stopping makes some things better. It’s worth doing but it’s very late in the game.” Similarly, if you only focus on friendships when your family and professional obligations slow, you will be at a disadvantage. Damage will have been done. The payoff in making friendship a priority was born out in the long-running Harvard Study of Adult Development, which followed more than 700 men for the entire course of their lives. What best predicted how healthy those men were at 80 wasn’t middle-aged cholesterol levels, it was how satisfied they were in their relationships at 50.8
Fortunately, it is possible to make new friends at every stage of life. In Los Angeles, I met a group of 70-something women who bonded as volunteers for Generation Xchange, an educational and community health nonprofit. The program places older adults in early elementary classrooms as teachers’ aids for a school year. As a result of the extra adult attention in class, the children’s reading scores have gone up and behavioral problems have gone down. The volunteers’ health has improved—they’ve lost weight, and lowered blood pressure and cholesterol. But they have also become friends, which is just what UCLA’s Seeman had in mind when she started the program. “One of the reasons our program may be successful is that we are motivating them to get engaged through their joint interest in helping the kids,” Seeman says. “It takes the pressure off of making friends. You can start getting to know each other in the context of the school and our team. Hopefully, the friendships can grow out of that.”
Concerns about loneliness among the elderly are well-founded. Demographics are not working in favor of the fight against loneliness. By 2035, older adults are projected to outnumber children for the first time in American history. Because of drops in marriage and childbearing, more of those older adults will be unmarried and childless than ever before. The percentage of older adults living alone rose steadily through the 20th century, and now hovers at 27 percent. And a digital divide still exists between older adults and their children and grandchildren, according to recent studies. That means older adults are less able to use virtual technology like Zoom to stay connected during the COVID-19 pandemic—though some are learning. Laura Fisher, a personal trainer in New York City, found that putting her business online meant training older clients one-on-one in videoconferencing. She now works out with one of her young clients in New York City and her client’s grandmother in Israel. Generally, older adults who use social media report more support from both their grown children and their friends. “For older people, social media is a real avenue of connection, of relational well-being,” says psychologist Jeff Hancock who runs the social media lab at Stanford University.
That is good news in this moment of enforced social isolation. So is the fact that being apart has reminded so many of us of how much we enjoy being together. For my part, I sent those flowers to my mother-in-law after all when I discovered contactless delivery. When the flowers arrived, we spoke again. And then I called her again two days later. “It’s great to talk to you,” she said.
Lydia Denworth is a contributing editor for Scientific American and the author of Friendship: The Evolution, Biology, and Extraordinary Power of Life’s Fundamental Bond.
Lead image: SanaStock / Shutterstock
References
1 Holt-Lunstad, J., et al. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspectives on Psychological Science 10, 227-237 (2015).
2 Silk, J.B., Alberts, S.C., & Altmann, J. Social bonds of female baboons enhance infant survival. Science 302, 1231-1234 (2003).
3 Holt-Lunstad, J., Uchino, B.N., Smith, T.W., & Hicks, A. On the importance of relationship quality: The impact of ambivalence in friendships on cardiovascular functioning. Annals of Behavioral Medicine 33, 278-290 (2007).
4 Uchino, B.N., Kent de Grey, R.G., & Cronan, S. The quality of social networks predicts age-related changes in cardiovascular reactivity to stress. Psychology and Aging 31, 321–326 (2016).
5 Seeman, T.E., et al. Social network ties and mortality among tile elderly in the Alameda County Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 126, 714-723 (1987).
6 Yang, Y.C., et al. Social relationships and physiological determinants of longevity across the human life span. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 113, 578-583 (2016).
7 Chopik, W.J. Associations among relational values, support, health, and well‐being across the adult lifespan. Personal Relationships 24, 408-422 (2017).
8 Vaillant, G.E. & Mukamal, K. Successful aging. American Journal of Psychiatry 158, 839-847 (2001).