I was not allowed to see the bones of the dead when I visited Jennifer Raff. They were fragments of teeth and skulls held in a small metal cabinet in the basement of Fraser Hall, the University of Kansas’ hub for anthropology research. The bones can be thousands of years old and belong to some of the earliest-known settlers of the Americas.
Raff, who practices martial arts, has a strong athletic build and a bright, unguarded demeanor. As we walked through the anthropology department above the basement, I noticed skulls of hominids in glass cases along the walls. So why were the bones in the basement so vigilantly out of bounds?
Raff told me that Native Americans typically regard the remains as sacred, belonging to their ancestors. Members of some tribes had granted Raff permission to study the genetic composition and origins of the bones. But she must do so discretely, keeping the remains hidden from visitors.
Raff, an associate professor of anthropology at the university, specializes in paleogenomics, extracting genetic material from ancient remains. The DNA preserved inside the remains has the power to vindicate or undermine carefully laid out archaeological theories about migration patterns, how and when people first arrived, and to shed light on how these early settlers lived their lives.
I can’t atone for the abuses of the past, but I can try to make the field better.
For years, Raff has studied how humans first set foot in the Americas. Her 2022 book, Origin: A Genetic History of the Americas, was praised by Dartmouth College paleoanthropologist Jeremy DeSilva for drawing together archaeology and Indigenous oral traditions “in a masterly retelling of the story of how and when people reached the Americas.”
Raff admitted that she was not always sensitive to the provenance of the ancient remains she studies. When she was working on her Ph.D., she analyzed DNA from a first-century burial site in Illinois without the consent of local tribes. She used rib bones belonging to deceased women and children to extract DNA and study relatedness. It was perfectly legal to use the skeletons, which were kept at Indiana University, but she now regrets doing so.
“In retrospect, I should have gone to tribes who claim descent from these populations, talked to them about the work, and gotten permission,” Raff said. “But at the time I thought, ‘Oh, it’s fine,’ so I just did it. That’s an attitude that I really push back against now with colleagues and other people in the field, thinking you can just do this work without permission or engagement with descendant communities. I really regard my earlier work as very unethical. I won’t go back and publish any of it.”
Raff’s change of heart toward ancestral remains and artifacts represents a personal awakening for her. It also represents a generational shift in the practice of anthropology and archaeology. Raff’s mentor, Dennis O’Rourke, a professor of anthropology at the University of Kansas, said that in previous generations archaeologists rarely if ever consulted with Indigenous peoples. “There were no seeking permissions to do the work,” he said. “Most researchers relied on museums to provide permissions, and museums sometimes engaged in consultations and sometimes not.”
As Raff and I arrived at her office, she said, “One of my missions as a scholar in this discipline is to try to improve it. I can’t atone for the abuses of the past, but I can try to make the field better in my way.”
Raff sat at her desk in her university office, pulling her dark hair into a ponytail behind her head. A framed photograph of Muhammad Ali boxing underwater in a swimming pool hung on a wall. A Rothko print in deep blues and reds hung on an opposite wall. Sitting on a bookshelf were prizes Raff has won for Origin, one of them from the American Anthropological Association for the best science book in the field of biological anthropology. They were joined by mostly popular science and adventure books from authors she admires: In the Empire of Ice by Gretel Ehrlich and Control: The Dark History and Troubling Present of Eugenics by British geneticist Adam Rutherford, a friend and mentor.
With the sun setting over the Kansas horizon, Raff told me it was a summer in the Arctic that shaped how she saw her own discipline. It was 2009 and she was a postgraduate, a geneticist invited to participate in the excavation of Nuvuk, an archaeological site located in Alaska’s northernmost point. Ocean storms continuously erode the coast there, pushing the frontier of the land southward. The area is home to the Iñupiat, who have lived there for more than 1,000 years.
The dig that Raff joined was excavating the ancient cemetery at Nuvuk, which was rapidly eroding into the water, taking away with it the cultural and physical remains of the paleo-Inuit who were most undoubtedly related to the present-day inhabitants of Utqiaġvik.
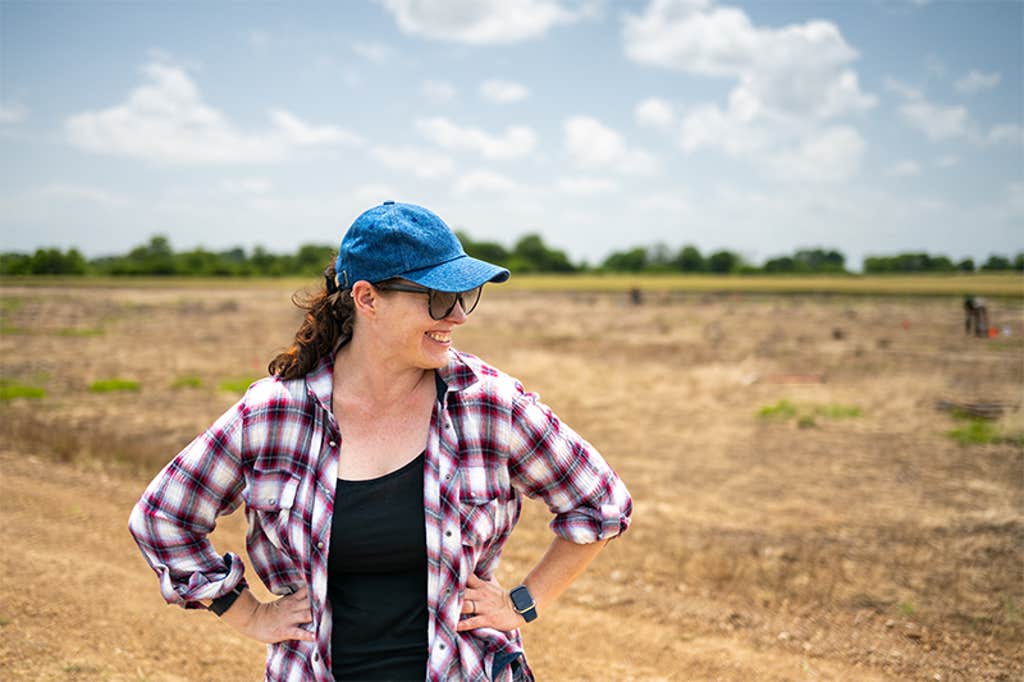

The Arctic landscapes left an indelible impression—the starkness of the open plains, the punishing swarms of insects, the winteriness even on the warmest days. “It’s a remarkable environment,” Raff said. The people whose genes Raff studies had survived this and harsher environments for at least a millennium. “I could really appreciate the innovations that kept them alive,” she said.
The scientists had sought permission to sequence the DNA preserved inside the remains unearthed at the cemetery through consultations with the Iñupiat of Utqiaġvik. The community had agreed, provided certain provisions—minimal physical damage to the excavated bodies, followed by prompt reburial.
“It was liberating,” Raff said. “To work within an explicitly stated framework, composed by the descendants of the peoples I was hoping to learn from, made it easy to do our scientific research on their terms.”
Since the 1800s, anthropology museums have stocked their collections with Native American artifacts and remains sacred to tribes. “Native peoples were essentially powerless to stop it,” said Chip Colwell, editor-in-chief of Sapiens, an anthropology magazine, and formerly a senior curator at the Denver Museum of Nature and Science. “When I was coming up in the field in the ’90s, it was extraordinarily rare for Native peoples’ concerns, insights, practices, and religions to be considered as a part of archaeology.”
Human history belongs to all humankind, the rationale went, elevating archaeology and anthropology to the prerogative of enlightening all humanity. From that vantage point, the needs and views of a relatively small group, such as the Native Americans, seemed trifling, especially if they insisted on the reburial of discovered bones and artifacts. Reburial, rather than preservation of archaeological finds in museums, was seen as anti-science, prohibiting future investigations which might shed new light on history.
In 1971, road workers discovered a burial ground in Glenwood, Iowa. They uncovered the remains of 26 European-American “pioneers” and a Native American woman and her child. While the pioneers were reburied in a local cemetery, the Native American remains were packed off to the Office of the State Archaeologist in Iowa City, to be distributed to museums or universities. “Dead Native Americans were archaeological resources for the state and white people weren’t,” Colwell explained. “We had allowed Native peoples to become the subject of science in a way we hadn’t for other people.”
The Glenwood incident sparked a movement to defend Native American rights, challenging archaeological standard practice. In 1990, on the heels of the Civil Rights movement, the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act (NAGPRA) was enacted into law. It gave Indigenous people the right to rebury their dead, provided they could make a tenable connection between ancient remains and tribal affiliation. Under NAGPRA, affiliation can be established via land ownership, so that remains discovered on federal or tribal land are recognized as belonging to the tribes themselves. At the time, Colwell said, passage of NAGPRA caused an uproar. “Some scholars equated reburial to book burning or destroying libraries of knowledge.”
Gradually, the culture among archaeologists began to shift, thanks largely to Indigenous activism. “That began to really push archaeologists to confront the ways in which their discipline was perpetrating harm,” Colwell said. He estimates that 90 percent of anthropologists and archaeologists today are on board with the law.
Raff said meeting tribal members and learning about their cultures from them is a boon to science. Scientists can’t approach research questions, such as when humans first arrived in the Americas “with just one discipline’s data and methods alone. You have to let multiple truths or multiple possibilities coexist at the same time.”
Raff’s comfort with ambiguity deeply informs her work. Her central thesis in Origin runs contrary to the anthropology that has long been taught in classrooms, a tidy story of how the first people arrived on the American continent in a single wave of migration from Asia some 15,000 years ago.
Raff patiently unwinds this expectation, explaining how multiple disciplines and ways of knowing have, over the past two decades, converged on a richer, but muddier narrative of when humans first set foot in the Americas. The tidy Clovis-first theory held that people who settled the continent about 15,000 years ago were supported by a novel technology—a special kind of sharp spearhead (a Clovis head) that allowed them to hunt and subsist on megafauna. It was assumed that the “last glacial maximum,” an ice age that lasted for 4,000 years (between 23,000 to 19,000 years ago), covered the land in deep, year-round ice sheets that prohibited settlers before then.
But studies of DNA from the oldest human remains unearthed in the Americas, as well as sequenced genomes of present-day Indigenous people, show that Native Americans are descendent from a single population, dating to somewhere between 25,000 to 20,000 years ago. This suggests there was a refugium—a hospitable nook where these ancestors survived—far from other human tribes roaming the plains of Asia over the same period.
Raff’s thesis about the first Americans runs contrary to the tidy story taught in classrooms.
There have been no confirmed human settlements that date to this time, although Raff believes the best place to look is underwater, not far from where she conducted her research in Nuvuk. Scientists know that during the last Ice Age, Asia was connected to North America by a land bridge across the Bering Strait, which may have had a climate mild enough to allow populations to flourish.
The genetic signatures also show a distinct spread of different tribes—a branching sometime between about 22,000 and 18,000 years ago. One branch, the Ancient Beringians, has no known living descendants. The other, known as the Ancestral Native Americans, gave rise to populations south of the Laurentide ice sheet, which cloaked the north of the continent, along a line roughly connecting present-day Seattle with New York City.
The Ancestral Native Americans spread quickly across the whole continent, with many populations splitting extremely rapidly from one another. In Origin, Raff explains how this has long baffled archaeologists because it is not consistent with a slow overland advancement of hunter-gatherer populations.
A hypothesis proposed by Canadian archaeologist Knut Fladmark in 1979 has gained significant traction in recent years due to the pairing of ancient DNA work and Indigenous knowledge. Fladmark argued that people could have migrated along a coastal route rather than an ice-free corridor inland. Further research by scholars, notably Jon Erlandson of the University of Oregon, has led to the theory that humans could have lived along the coast eating kelp, fish, shellfish, and marine mammals, traveling to new sites by boat, via a “kelp highway,” which ran north to south along the west coast of North America, a route that could account for the rapid spread of communities.
This idea lacks concrete archaeological evidence—no physical artifacts related to navigation have been found—but is supported by oral traditions of the Tlingit and Haida tribes of Alaska, “who maintain that their ancestors were a seafaring people who have lived in this region since the dawn of history,” Raff writes in Origin. The oral traditions of the Tlingit are rich in narratives of ancestors traveling along the Pacific Northwest Coast and down the Stikine River, over and below glaciers, foraging for seals and other marine mammals.
In 2007, a genetic reconstruction of the genome of Shuká Káa, a man whose skeleton was found in an Alaskan cave and was dated to 10,000 years ago, added credibility to the kelp highway theory. It showed that Shuká Káa’s people were the ancestors of the Tlingit. At the same time, chemical analysis of his teeth showed that Shuká Káa had indeed grown up on a diet of seafood. Other archaeological artifacts found alongside his body in the cave suggested that he had engaged in long-distance trade for high quality stone, further support the coastal highway theory. The genetic sequencing work was done in consultation with the Tlingit tribe, and after the work was completed, Shuká Káa was buried in 2008.
Raff reminds her readers that not all Native American origin stories align neatly with the results of genetics. And that genetic results are not set in stone, as new techniques overturn initial interpretations. In the closing pages of Origin, Raff calls it hubris to think a definitive history of the peopling of the Americas is possible.
Raff ventured into writing for the public in 2015 when she created a blog called Violent Metaphors. The name, suggested by a publicist friend, reflected her feisty feelings at the time. “I wanted to go after pseudoscience and the anti-vaccine stuff that really made me mad,” she said. One post about misinformation about measles’ vaccinations begins, “Dear parents, you are being lied to.” “I learned the things that went viral were the ones that I was writing passionately about,” Raff said. “When I had a real connection, emotional connection to a topic, I wrote the best.”
Raff’s blogging landed her in the culture wars, where she became a target for those who saw her as an embodiment of political correctness over objective science. In particular, Raff has been in the crosshairs of Elizabeth Weiss. Weiss is a professor emeritus of anthropology at San Jose State University and the coauthor with James W. Springer of Repatriation and Erasing the Past. Weiss and Springer criticize NAGPRA and the reburial of human remains in ancestral burial grounds. They argue “secular and scientific scholarship concerning human and biological differences” is being suppressed and censored by deference to Native American religious myths.
I don’t want to be this white savior liberal girl running around.
In a 2022 review of Origin in the online magazine Quillette, Weiss aimed that criticism at Raff. “To defer to Indigenous creationist ideas is no different, in principle, from deferring to religious Christian attitudes,” Weiss wrote. As “an anthropologist, I find the anti-scientific trend that the book represents to be deeply unsettling.”
In response, Raff said, “Being respectful of the beliefs and priorities of Indigenous peoples is not in opposition to science, and I’ve never been asked by any tribe to change the results of our research to fit an agenda. Weiss is stereotyping Native Americans as anti-science, which is ludicrous; they are as varied in their perspectives and belief systems as all people are.”
Raff was born Jennifer Anne Kedzie in Carbondale, Illinois, the first daughter of three. Her youngest sister died in infancy of spinal muscular atrophy, a rare genetic disorder for which there was no cure in the early 1980s. Raff was 4. After the loss of her daughter, Raff’s mother was moved to return to higher education and neuroscience, and the family lived in university towns in Missouri and Indiana. Raff’s parents divorced amid the moves and financial struggles, but Raff stayed close with both her parents. Raff’s father worked as a quality assurance engineer in industry, and she credits him for pushing her to look for answers and research. “Every time I would ask him a question, he would be like, ‘Look it up.’”
On the campus of Indiana University where she lived as a student, Raff grew close to Elizabeth and Rudolf Raff, both biology professors. Rudolf Raff was a pioneer of evolutionary developmental biology and director of the Indiana Molecular Biology Institute. Their son, Aaron, was Jennifer’s boyfriend, and Aaron and Jennifer married while she was in college but divorced during her last year of graduate school. “It was horrible, a really hard time,” Raff said. “But I got through it. I focused on martial arts and fighting. I thought, ‘This could be a life for me.’” And then I thought, ‘No, you know what? I love science more.’” She kept Raff as her surname.
Raff has never lived outside the inland heart of the country—Illinois, Indiana, Utah, Texas, and now Kansas. Raff’s home is decorated with objects embedded with personal meaning—sepia photographs of her family, traditional weapons used in martial arts, and a handful of paintings. “Low Tide,” a peaceful landscape work by the Native American artist Linda Infante Lyons, hangs above the dining room table. It is also on the cover of Origin. A violent depiction of abolitionist John Brown leading a bloody uprising against enslavers in 1865 hangs in the living room.
In the time I spent with Raff, there was only one instance I saw her look incredibly uncomfortable. It came during a dinner at her home with her husband, Colin McRoberts, a lawyer and negotiations consultant; their son, Oliver; her mother, Kathy; and a friend of Raff’s, Peter Koenig. As we discussed the success of Origin and Raff’s advocacy for the inclusions of Native Americans’ own stories in archaeology, Koenig remarked, “It took a white girl for Americans to hear the story.” Raff buried her head in her hands and hoodie.
“I don’t want to be this white savior liberal girl running around,” Raff told me later. “I think I have a platform. I don’t know if it’s because I’m white, because I’m a professor, because I’ve been writing for the public for a long time. I don’t know. It might be all these things.”
In the spring of 2024, Raff received a Guggenheim Fellowship to complete her second book, The Ancients: The Untold Story of How We Became Human. “It will continue my focus on challenging pernicious concepts of biological race and colonialist practices—particularly those still prevalent in paleoanthropology and paleogenomics,” Raff said. It will continue her quest to “complicate” the picture of human origins, so the public can begin to see the complex narratives of belonging. Where an origin is not a single point on a distant horizon, but a forest of interwoven roots. ![]()
Lead image: Zichrini / Shutterstock