While on vacation in distant locales, people often find that time moves quite differently than in the places they’re used to. In the tropics, we settle into the grooves of “island time” and relax thanks to a more leisurely rhythm. A trip to a big city can leave us exhilarated but also drained by the energetic whir of life there.
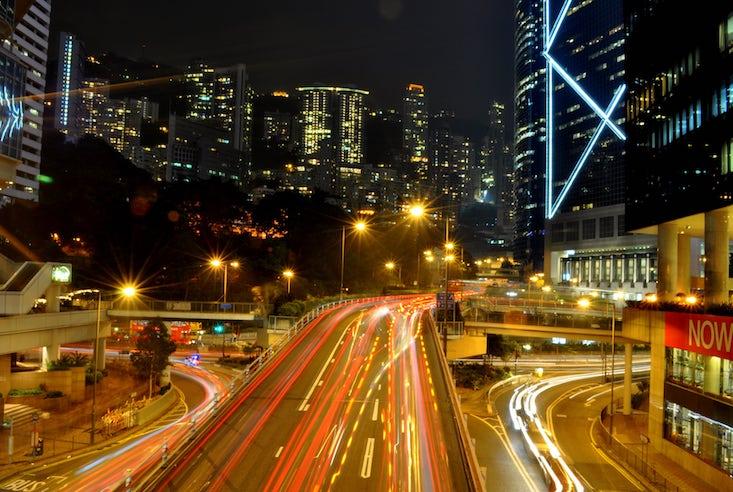
The different paces of different communities also seem to be connected to other cultural characteristics. Robert Levine and his colleagues have studied the speed of life in cities around the world and across the U.S. In a series of experiments they measured how fast solitary pedestrians in a downtown core covered a distance of 60 feet (being careful to exclude those who are obviously window shopping), timed how long it took to complete a simple commercial transaction, and recorded the accuracy of randomly selected clocks in the downtown business area. They found that places with a faster pace of life also had more robust economies (as measured by GDP per capita, average purchasing power, and average caloric intake), and that people in larger cities tended to move faster than those in less populated areas. They also found truth to the stereotype that people move slower in hotter places.
So as you might expect, fast-moving people are associated with fast-moving economies. But does that faster life translate into greater happiness? In faster places (specifically, economically developed areas of North America, Western Europe, and Asia), people were more likely to smoke, less likely to take the time to help strangers in need, and more likely to die from coronary heart disease. Yet Levine and his colleagues found that residents in faster places tended to report feeling somewhat happier with their lives than those who lived in slower places. A city’s pace of life was indeed “significantly related” to the physical, social, and psychological well-being of its inhabitants.
Perhaps the higher reported rates of happiness simply reflect the fact that faster places have more robust economies. But the relationship between income and reported happiness is far from obvious. According to the “Easterlin paradox” (named after economist Richard Easterlin), once people have enough money to meet their basic needs, having more money is not necessarily correlated with higher self-reported happiness. Easterlin’s claims are controversial and not universally accepted; even if his theory is correct, wealthier nations might be happier overall if they address the basic needs to more of their people. In any case, the ongoing debate indicates that we need to tread carefully when making connections between happiness and overall economic factors.
Among individuals in a society, busyness—or the feeling of busyness—seems to be an important factor in well-being. That feeling of busyness—of having a lot to do and too little time in which to do it is often associated with stress and anxiety. However in many contexts being “busy” is badge of honor: Busy parents are seen as devoted to their children’s well-being, the busy real estate agent must be closing lots of sales, and the busy lawyer can charge a premium hourly rate. In U.S. studies, the happiest people reported that they were busy, in the sense that they had little excess time, yet did not feel rushed. Like big-city dwellers, they seemed to thrive at a faster pace.
Levine’s work raises the intriguing possibility that an individual’s feelings about their use of time contribute as much or more to their happiness as does economics. Now the big challenge is to find out which way the causal chain works: Does the feeling of being active, yet not rushed, contribute to happiness? Or does happiness allow people to perceive their use of time in positive ways?
Jeanette Bicknell, Ph. D., is the author of Why Music Moves Us (2009). She lives in Toronto, Canada.
WATCH: The direction in which time flows.
 M.I.T. professor of physics” data-credits=”” style=“width:733px”>
M.I.T. professor of physics” data-credits=”” style=“width:733px”>
This classic Facts So Romantic post was originally published in January 2014.