As a rule, huge organizations move sluggishly, bogged down in democratic decision-making processes and bureaucratic policies. Ebola, on the other hand, moves fast. People become desperately sick and contagious within a few weeks of infection. By the time international agencies effectively responded to the ongoing Ebola outbreak, it had spiraled out of control in West Africa.
Although the rate of infection has now slowed in Sierra Leone and Guinea—and appears to have halted in Liberia—the Ebola virus has claimed the lives of more than 10,000 people to date. Had the international response been more responsive to the shifting situation, more organized, more trusting of infectious-disease experts, and braver and bolder early on, the death toll might not have been so high, the operation so expensive. From a distance, the plodding pace of the international Ebola response is understandable given the constraints of the system. But people who witnessed the outbreak up close—although thankful for the good will—tend to be less forgiving.
The gallery that follows is a timeline, of sorts, of the response to the disease. I reported and shot this story over the course of two month-long visits to Sierra Leone in December 2014 and February 2015.
THE OUTBREAK BEGINS

March 14, 2014: Tales of an unknown disease emerge from the tropical forest of Guinea, a small Francophone country in West Africa. A Guinean newspaper reports on eight patients afflicted with “anal and nasal bleeding.” (Months later, an investigation finds that the disease began with a boy who fell sick in a remote region of Guinea in late December 2013.)
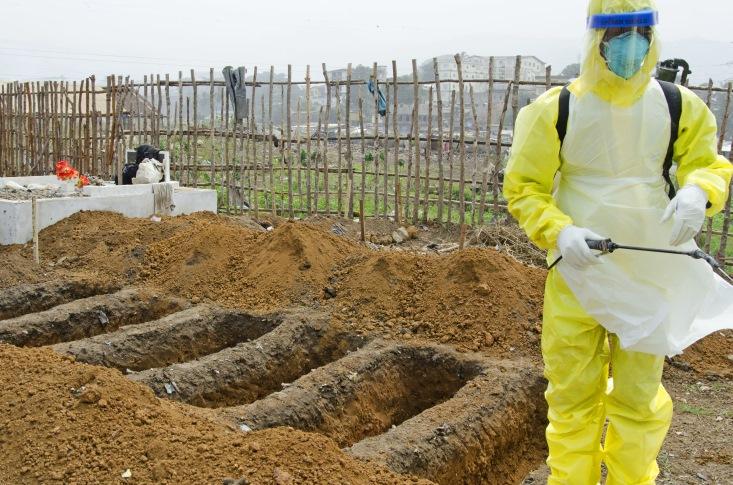

March 31, 2014: 114 cases of Ebola are confirmed in Guinea and Liberia, along with 72 deaths
An official with the aid organization Doctors without Borders warns of an Ebola “epidemic of a magnitude never before seen.” The World Health Organization counters that the outbreak is relatively small (pdf) compared with those in the past.
1 MONTH SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
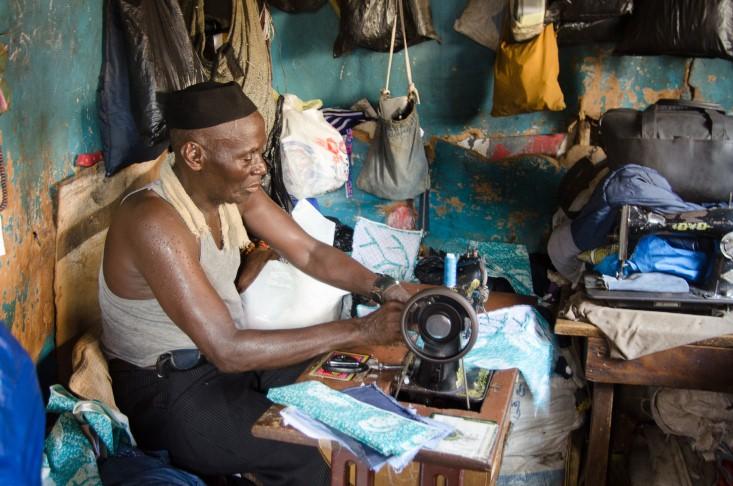

April, 2014: Mining companies in Guinea lock down operations and evacuate foreign staff. Two months later, those in Sierra Leone follow suit. Governments in the three nations hit hard by Ebola lose revenue as international operations close and trade between the countries grinds to a halt. Household incomes plummet as curfews and checkpoints, meant to contain Ebola, shut sellers off from markets. By June 11, nearly half of those working in Liberia when the outbreak was first detected, in March, no longer have jobs (pdf). Nearly everyone complains that business is down.
Ebola’s economic impacts could stretch far into the future. According to a recent report from the United Nations Development Group (pdf), the epidemic is likely to raise poverty rates in already poor communities, due to declining incomes and the rise in food prices.
3 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES

June 11, 2014: 467 Ebola cases, 246 deaths in Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia
Sierra Leone closes schools and colleges to slow the spread of Ebola, as have Liberia and Guinea. Educational programs air on the radio, but some mothers say their young children cannot tune in since they must accompany the women to work at markets and farms.
5 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
Health workers in the three countries die in droves from Ebola. In August, nurses strike because of a lack of protective gear and pay.
5 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES

August 8, 2014: 1,766 Ebola cases and 959 deaths in Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia
The WHO declares Ebola an international health emergency. With this declaration, the slow process of organizing and funding a worldwide campaign against the virus begins.
6 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
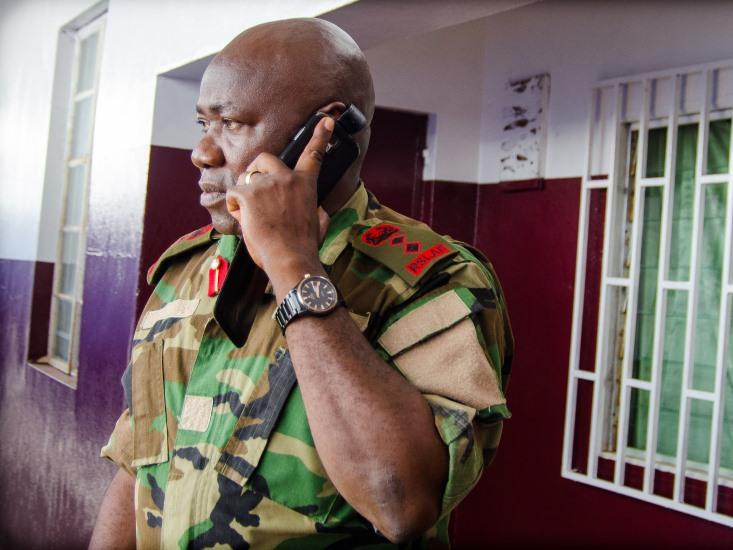

September 5, 2014: 3,944 Ebola cases, 2,097 deaths in Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia
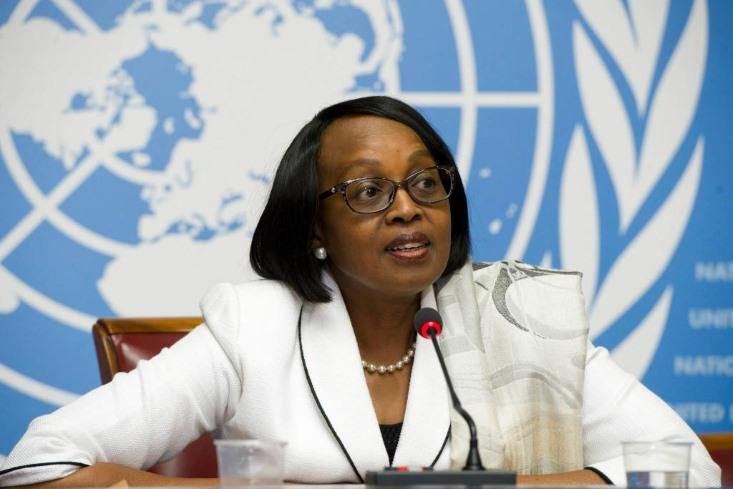
With support from doctors in the three hard-hit countries, the WHO recommends clinical trials to see if the blood from Ebola survivors can treat the disease.
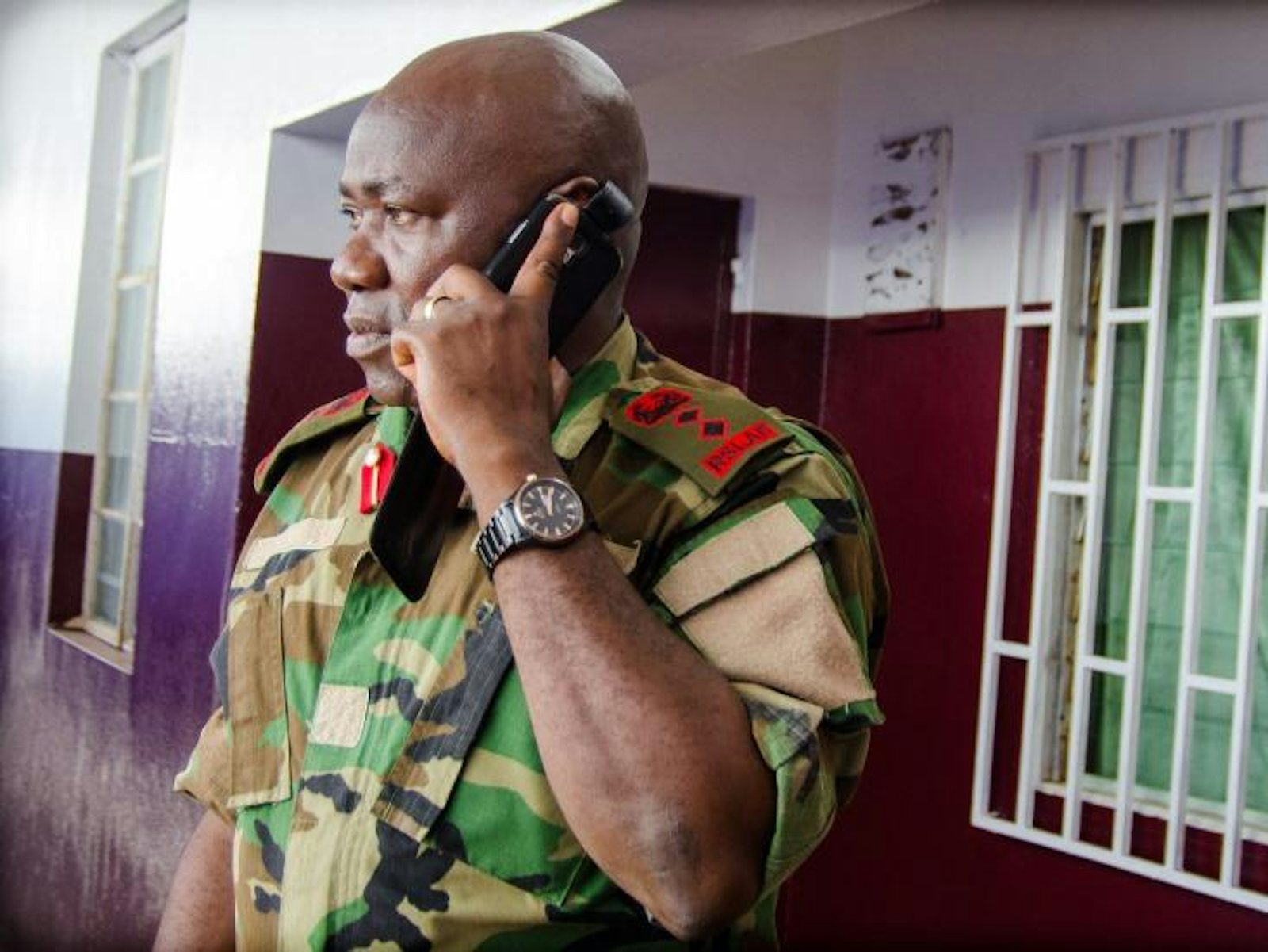
By December 8, the number of Ebola cases has increased more than four-fold since the WHO’s recommendation, to 17,800. Funds for studies on survivor blood have been promised, but have not yet hit the ground. Anxious after watching their colleagues and countrymen die, Foday Sahr (above) and a few other researchers in Sierra Leone begin the trial on survivor blood regardless. “I just wish the study had started earlier when the epidemic was at its peak,” Sahr says.
Kadiatu Fofanah (below) is one of the patients who receives an infusion of survivor blood; she goes on to survive the disease as well.
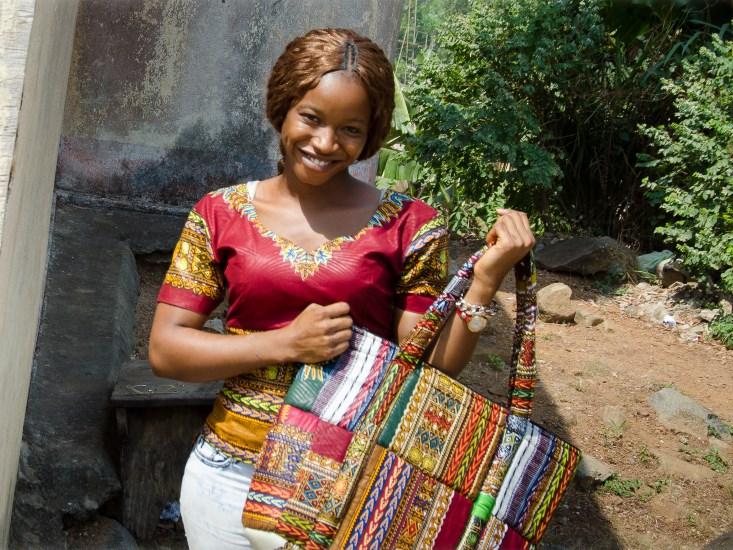

December 4, 2014: Kadiatu Fofanah feels weak.
December 5: Fofanah begins to vomit and have diarrhea.
December 10: Fofanah feels extremely sick, checks into the 34th Military Hospital in Freetown, Sierra Leone, and learns she is Ebola positive.
December 12: A military doctor offers Fofanah an infusion of Ebola survivor blood as part of a study, and she accepts.
January 20: Fofanah is discharged from the hospital as an Ebola survivor.
8 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
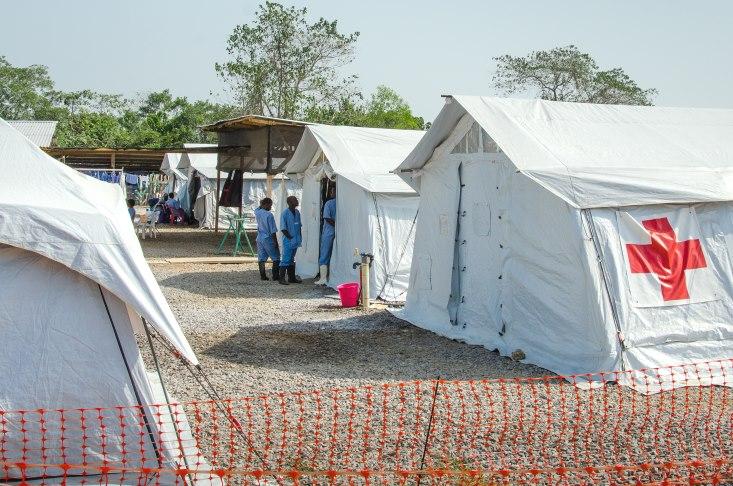

November 1, 2014: Months after a tidal wave of Ebola pummeled the main hospital in Kenema, Sierra Leone, in July, August, and September, an Ebola treatment unit run by the International Federation of the Red Cross opened nearby.
9 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
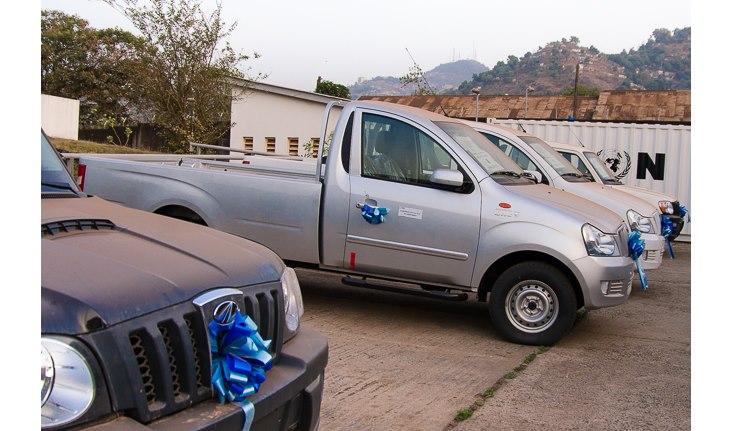

In late December, funds for the Ebola response finally translate into enough ambulances, staff, and hospital beds needed to handle the contagion in Sierra Leone. With this surge in capacity to treat Ebola, along with a strong push from within communities to stop the spread of the virus through bodily contact, the virulent spread of Ebola slows by early January.
The UK provided a large portion of Ebola funds to Sierra Leone through its Department for International Development. In a hearing on their spending held in December, parliamentarians asked why donations were committed mainly in the fall rather than as early as May, before the outbreak spiraled out of control. The hearing report reads that there was “an unfortunate time lag between the Department’s recognition that it had to act and its allocation of funding to deal with the outbreak… Had the Department acted sooner, both lives and money would have been saved.”
10 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
New vehicles and treatment tents continue to arrive in January and February, yet they remain unused because they’re no longer in demand.
11 MONTHS SINCE FIRST CONFIRMED CASES
February 28, 2015: 23,725 Ebola cases and 9,660 deaths in Guinea, Sierra Leone, and Liberia
Since February, Sierra Leone has accounted for about two-thirds of the new Ebola cases around the world. Within the country, the district of Port Loko became a hotspot after a December ban on maritime activities was lifted. In response, Sierra Leone’s president stopped the ferry from operation on February 28, soon after I shot this video. On the same day, the vice president placed himself under quarantine after one of his bodyguards died of Ebola.
On the day before this story was published, the Ebola toll registered at 24,666 cases and 10,179 deaths. Because some people go unaccounted for, that is almost certainly an underestimate.
Travel for this story was paid for by a grant from the Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting.
Amy Maxmen is a science journalist who writes for Nautilus, Newsweek, National Geographic and other magazines.