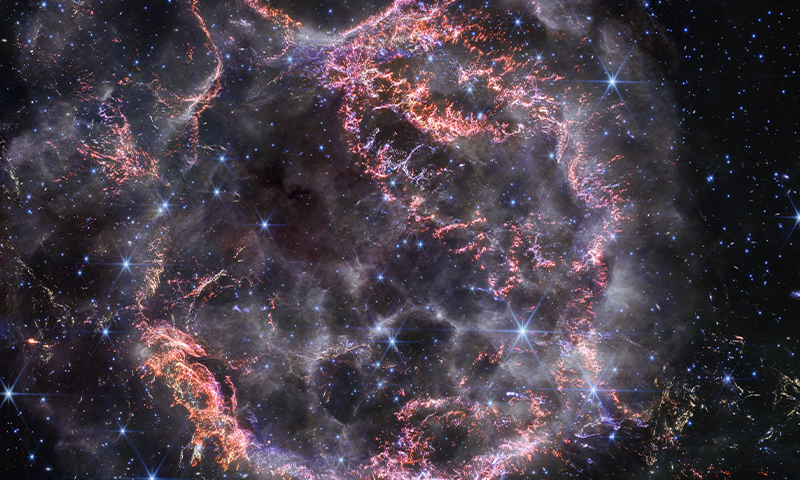
Cassiopeia A is one of the most thoroughly studied supernovas in the cosmos. It spans 10 light-years across, or 60 trillion miles. Over the years, numerous ground observatories and telescopes have assembled pictures of the remnants of this exploded star. Now the James Webb Space Telescope is providing a new high-definition look at Cas A.
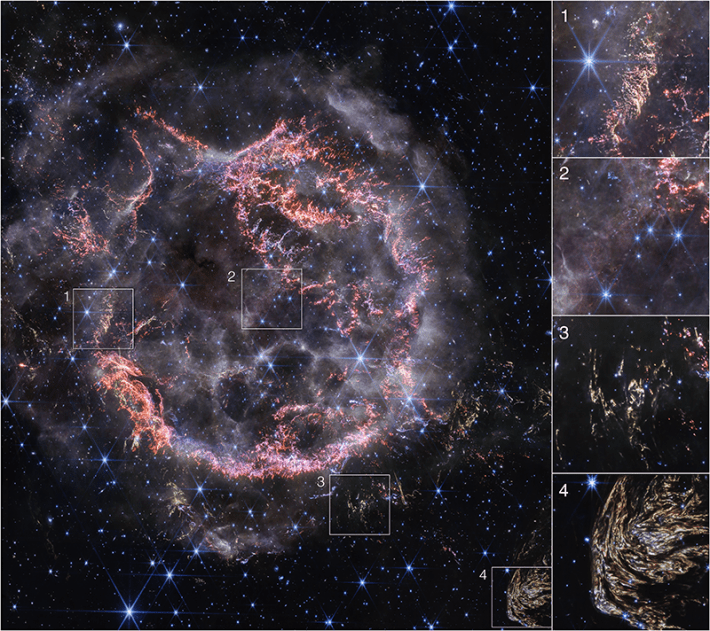
The near-infrared image shown here, with insets, was taken in December 2023 and offers some clues to the dynamics of the dying star’s explosion. It shattered almost like glass, leaving behind tiny shards of star material, explained Danny Milisavljevic of Purdue University, who leads the research team, in a NASA statement.
Stars burn nuclear fuel at their cores, generating outward pressure that resists the inner squeeze of gravity. But when a star runs out of fuel, it cools rapidly and can no longer resist that gravitational pull. The star rapidly collapses, which sends out shock waves that cause the outer part of the star to explode. The dense core usually remains, surrounded by an expanding cloud of hot gas called the nebula.

1. Tiny knots of gas, made of sulfur, oxygen, argon, and neon from the star itself are shown here in bright pink and orange. Some strands of debris are less than 10 billion miles across and too tiny to be detected. Researchers say these strands provide evidence that the star’s explosion was akin to the shattering of glass.
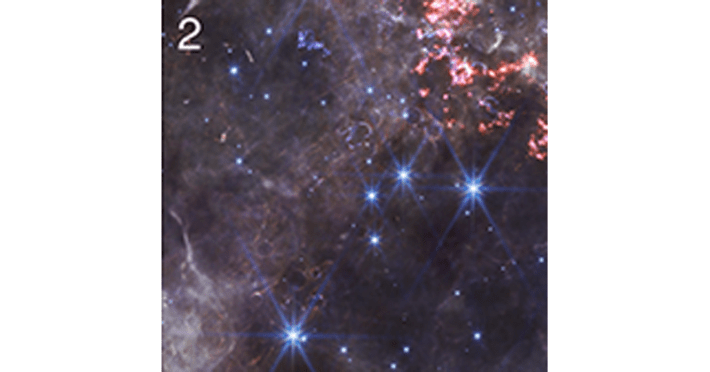
2. Circular filaments of white and purple seen here represent ionized gas found within the so-called Green Monster, a whorl of green light in Cas A’s interior that does not itself appear on this image. Researchers believe debris from the explosion of the star chiseled these white and purple circles into the gas emitted by the star before the explosion.
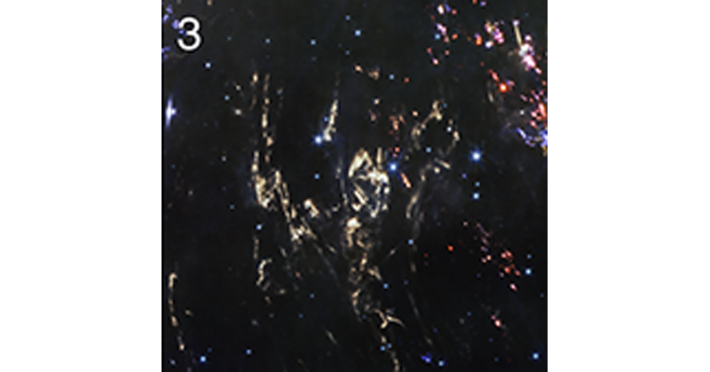
3. One of a few visible light echoes, which occur after light from the star’s explosion heats up cosmic dust, which then glows as it cools down.
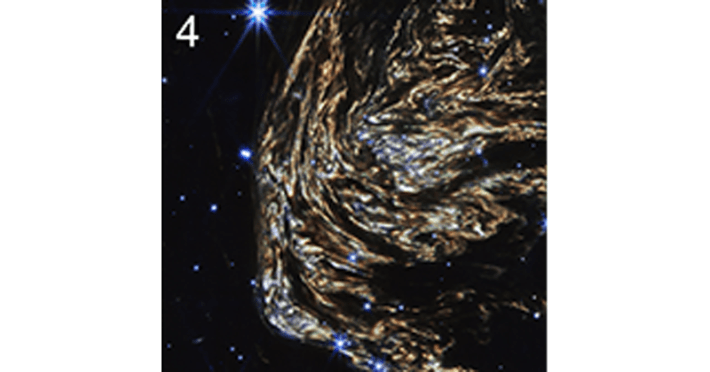
4. Nicknamed Baby Cas A, this large, striated splotch represents a light echo located about 170 light-years behind the exploded star. ![]()
Lead image: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, D. Milisavljevic (Purdue University), T. Temim (Princeton University), I. De Looze (University of Gent)